The Importance of Prototyping Your Products
- User validation: Prototyping allows you to validate your product concept with real users, ensuring it meets their needs and expectations before committing significant resources to development.
- Iteration: Creating a prototype enables you to iterate on your design, refining and improving it based on user feedback and testing results.
- Risk reduction: Prototyping reduces the risk associated with launching a new product, as it helps identify and address potential issues before they become costly problems during development or after launch.
- Team alignment: A prototype serves as a tangible representation of your product vision, helping align your team around a shared understanding of the product's goals and requirements.

Types of Prototypes
Low-Fidelity Prototypes
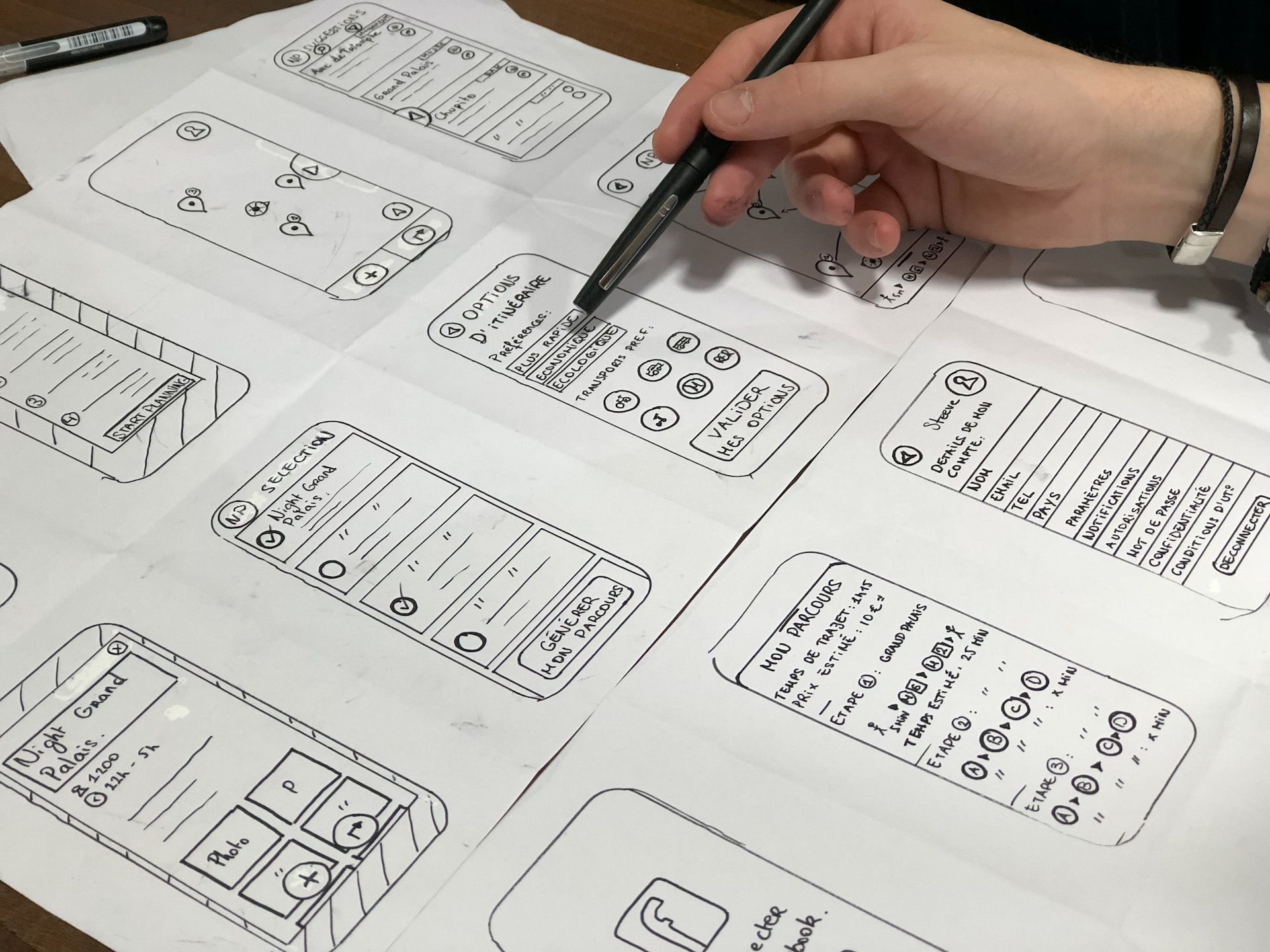
- Paper prototypes: Hand-drawn sketches or printouts that represent the product's user interface and functionality.
- Wireframes: Basic digital representations of the product's layout, using simple shapes and placeholders for content and functionality.
- Clickable prototypes: Interactive wireframes or mockups that allow users to navigate through the product's interface and perform basic tasks.
High-Fidelity Prototypes
- Interactive mockups: Detailed, pixel-perfect representations of your product's user interface, complete with visuals, animations, and interactions.
- Functional prototypes: Fully functioning versions of your product, built using actual code and incorporating the product's intended features and functionality.
Best Practices for Product Prototyping
1. Set Clear Goals and Objectives
2. Choose the Appropriate Level of Fidelity

3. Involve Users Early and Often
4. Iterate and Refine Your Prototype
5. Document Your Findings and Insights
6. Communicate Your Prototype's Purpose and Limitations
7. Don't Overthink It
Examples of Successful Prototyping
- Apple: Apple's product development process is famously secretive, but it's known that the company places a strong emphasis on prototyping. In the development of the first iPhone, Apple reportedly created numerous prototypes, testing and refining the device's design and functionality before settling on the final version that would revolutionize the smartphone industry.
- Airbnb: In the early days of Airbnb, the founders used a low-fidelity prototype – a simple website with basic functionality – to test their idea and gather user feedback. This initial prototype allowed them to validate their concept and refine their offering before investing heavily in development.
Mastering Product Prototyping

Related Courses
AI Prototyping for Product Managers
Build your first AI prototype next week -- even if you have no coding skills
Prototype to Production: The AI PM Playbook
Build, evaluate, and ship successful AI products with real-world frameworks and hands-on experience to become an advanced AI product leader
Technical Foundations & AI Prototyping for Product Managers
Two related skills in one course: master tech to speak the same language with your team. Use it to AI-prototype features or a side project.
Essentials of Product Management - HK version
Learn the skills & tactics to become a world-class PM, build winning products, and go after global PM opportunities with confidence.
Insight Driven Product Management for Growth - Scale Impact in any Organization
You'll analyze patterns between datasets and interpret data to uncover insights. You'll master strategic thinking and product execution.
You might also like

Becoming a Top Product Manager: Tips for Accelerating Your Career Growth

Mastering Competitive Positioning: A Comprehensive Guide for Product Managers

User Research: Selecting the Right Method